科研賦能:SP-ICP-MS與SC-ICP-MS技術(shù)的煥新升級(jí)之旅

ICP-MS是目前應(yīng)用最廣泛的原子光譜技術(shù)之一, PerkinElmer積極倡導(dǎo)的Single Particle單顆粒(SP)ICP-MS和Single Cell單細(xì)胞(SC)ICP-MS技術(shù),隨著前處理和實(shí)驗(yàn)技術(shù)、ICP-MS儀器及其數(shù)據(jù)處理軟件的不斷發(fā)展,正越來越多受到環(huán)境、食品、藥物、醫(yī)學(xué)、材料和工業(yè)等領(lǐng)域的關(guān)注和使用,幫助高校、科研機(jī)構(gòu)和政府實(shí)驗(yàn)室老師研究納米顆粒、微納塑料、細(xì)胞、微生物等微粒子,助力老師們不斷探索和創(chuàng)新。
SP-ICP-MS工作原理
SP-ICP-MS的工作原理是將分散在溶液中的納米顆粒物引入ICP-MS的離子源,單個(gè)納米顆粒在高溫等離子體中瞬時(shí)形成一束含特定元素的離子流,通過四極桿質(zhì)量分析器的掃描分離,在檢測(cè)器中產(chǎn)生特征元素的脈沖信號(hào)峰,根據(jù)脈沖信號(hào)峰個(gè)數(shù)與粒子數(shù)量、脈沖峰強(qiáng)度與粒子粒徑的正相關(guān)關(guān)系,獲得目標(biāo)顆粒物的數(shù)量、粒徑等信息。它能同時(shí)獲得納米顆粒濃度與粒徑分布、團(tuán)聚信息,能快速定量粒子內(nèi)外特定元素含量,具有靈敏度高、選擇性強(qiáng)等優(yōu)點(diǎn),是一項(xiàng)新興納米顆粒定性和定量的檢測(cè)方法。

SP-ICP-MS分析技術(shù)的核心是需要ICP-MS具有快速時(shí)間分辨能力。PerkinElmer NexION系列ICP-MS,最快瞬時(shí)采集速率達(dá)100 000點(diǎn)每秒,可直接表征小粒徑、多成分或多形狀的納米材料,如10nm Au NPs數(shù)量和粒徑測(cè)定、金納米棒的長短分析[1]、Au-Ag核-殼型納米顆粒在光照和外界環(huán)境中的轉(zhuǎn)變表征[2]、無需消解直接快速測(cè)量上千根單壁碳納米管中殘留金屬釔(常用催化劑)[3]、半導(dǎo)體有機(jī)溶劑中超痕量雜質(zhì)顆粒物[4]等;在環(huán)境研究方面,SP-ICP-MS可用于定量評(píng)價(jià)NPs在河流中的溶解動(dòng)力學(xué)[5]、CeO2?NPs在土壤基質(zhì)中的變化[6]、通過測(cè)定碳13同位素篩選測(cè)定微塑料[7]等;在食品、農(nóng)作物毒理研究方面,SP-ICP-MS可測(cè)定海養(yǎng)殖的雙殼類軟體動(dòng)物中金屬基納米顆粒[8]、探索納米氧化鈰暴露對(duì)大豆植物生長影響[9]等;在生命科學(xué)方面,SP-ICP-MS可評(píng)價(jià)海藻中TiO2 NPs的累積程度[10]、CuO NPs對(duì)土壤微生物群落的生態(tài)毒理效應(yīng)[11];而在醫(yī)學(xué)領(lǐng)域,SP-ICP-MS可量化NPs的暴露水平并做風(fēng)險(xiǎn)評(píng)估,如追蹤生物體液中金屬基NPs的行為[12],同時(shí)可作為標(biāo)記物判斷疾病,如與磁免疫測(cè)定法結(jié)合測(cè)定肺癌中腫瘤生物標(biāo)志物[13]等。
以單個(gè)細(xì)胞為單位,發(fā)現(xiàn)細(xì)胞個(gè)體間的差異對(duì)于闡釋相關(guān)金屬在細(xì)胞內(nèi)的遷移轉(zhuǎn)化及其毒理也十分重要,基于SP-ICP-MS技術(shù)的單細(xì)胞SC-ICP-MS技術(shù),將含特定元素的細(xì)胞視為一個(gè)整體,通過單細(xì)胞專用進(jìn)樣系統(tǒng)引入檢測(cè),實(shí)現(xiàn)含特定元素細(xì)胞的數(shù)量及單個(gè)細(xì)胞中元素含量測(cè)定。SC-ICP-MS能監(jiān)測(cè)含特定金屬元素的細(xì)胞個(gè)數(shù),測(cè)定細(xì)胞中金屬含量,有效評(píng)估細(xì)胞個(gè)體差異,能作為細(xì)胞特異性識(shí)別工具。在生命科學(xué)方面, SC-ICP-MS可監(jiān)控藻類細(xì)胞對(duì)NPs和金屬離子攝入行為[14]、可對(duì)金屬元素標(biāo)記的單細(xì)菌細(xì)胞進(jìn)行識(shí)別和計(jì)數(shù)[15]等;在醫(yī)藥學(xué)研究領(lǐng)域,SC-ICP-MS既能量化細(xì)胞中金屬含量,如SC-ICP-MS同時(shí)計(jì)數(shù)含Cu人血紅細(xì)胞及其Cu含量[16],又能給無機(jī)元素相關(guān)藥物開發(fā)與給藥提供指導(dǎo)意見,如通過SC-ICP-MS測(cè)定抗癌藥物單核Ir和雙核Ir(III)化合物在單個(gè)癌細(xì)胞的攝入和排出情況,首次量化證實(shí)雙核Ir(III)化合物的光催化抗癌效果更好[17]等。
△Asperon? 單細(xì)胞進(jìn)樣
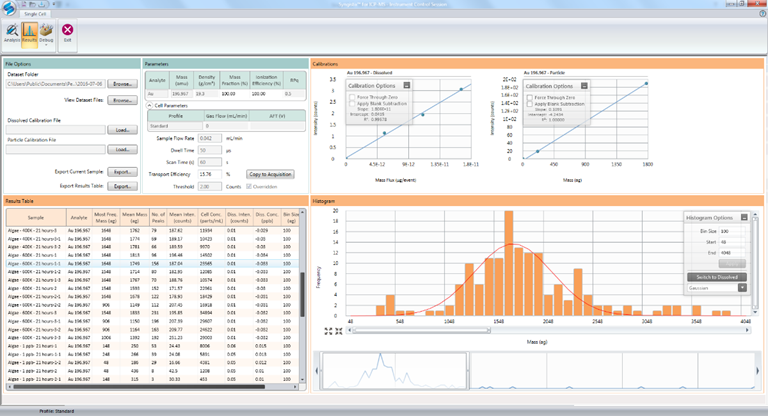
△單細(xì)胞ICP-MS分析

即刻獲取應(yīng)用合集
參考文獻(xiàn)
[1]Dimensional characterization of gold nanorods by combining millisecond and microsecond temporal resolution single particle ICP-MS measurements. G′abor Galb′acs. Department of Inorganic and Analytical Chemistry, University of Szeged, D′om square7, 6720 Szeged, Hungary. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry 2017
[2]Transformations of Gold-Silver Core-shell Nanoparticles in Exposure Media Measured by SP-ICP-MS. Ruth Merrifield,Jamie Lead,Center for Environmental NanoScience and Risk (CENR),Arnold School of Public Health,University of South Carolina,Chady Stephan,PerkinElmer, Inc. PerkinElmer Application Note 2016
[3] Analysis of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes with SP-ICP-MS. Jingjing Wang,James F. Ranville,Department of Chemistry and Geochemistry,Colorado School of Mines,Golden, CO. PerkinElmer Application Note 2017
[4] Analysis of Iron Nanoparticles in Organic Solvents Used in the Semiconductor Industry Using Single Particle ICP-MS in Reaction Mode. Chady Stephan,PerkinElmer, Inc. Shelton, CT. PerkinElmer Application Note 2022
[5] Quantitative Evaluation of Nanoparticle Dissolution Kinetics using Single Particle ICP-MS: A Case Study with Silver Nanoparticles.Denise Mitrano James F. Ranville Department of Chemistry and Geochemist ry Colorado School of Mines Golden, CO USA Chady Stephan PerkinElmer, Inc. Shelton, CT. PerkinElmer Application Note 2014
[6] A Sensitive Single Particle- ICP-MS Method for CeO2 Nanoparticles Analysis in Soil during Aging Process. Honglan Shi.Missouri University of Science and Technology, Chemical Department, Energy and Environment Research Center, J. Agric. Food Chem 2021
[7] Unlocking Carbon-13 with Single Particle ICP-MS: Feasibility Study for Microplastic Detection.Francisco Laborda Celia Trujillo University of Zaragoza Zaragoza, Spain Ryszard Lobinski Université de Pau et des Pays de L’Adour Pau, France. PerkinElmer Application Note 2022
[8] Ultrasound assisted enzymatic hydrolysis for isolating titanium dioxide nanoparticles from bivalve mollusk before SP-ICP-MS. A.Moreda-Pineiro. Chemistry School of Santiago de Compostela University in Spain. Analytica Chimica Acta 2018
[9] Effect of nano cerium oxide on soybean(Glycine max L. MERRILL)crop exposed to environmentally relevant concentrations. Hudson W. P. de Carvalho, School of Engineering, University of Guelph. Thornbrough Building, 50 Stone Rd E, Guelph,Ontario, N1G 2W1, Canada. ChemoSphere 2020
[10] Titanium dioxide nanoparticles assessment in seaweeds by single particle inductively coupled plasma-Mass Spectrometry.Antonio Moreda-Pi?neiro.Chemistry Department, Santiago de Compostela University, Spain. Talanta 2021
[11] Ecotoxicological effects of copper oxide nanoparticles (nCuO) on the soil microbial community in a bisoids-amended soil. Ajith Dias Samarajeewa,Soil Microbial Assessment and Genomics Laboratory, Biological Assessment and Standardization Section, Environment and Climate Change Canada. Science of the Total Environment 2020
[12] Assessing the Fate of Nanoparticles in Biological Fluids using SP-ICP-MS.Ciprian-Mihai Cirtiu Normand Fleury National Public Health Institute of Quebec (INSPQ), Canada Chady Stephan PerkinElmer, Inc. Shelton, CT. PerkinElmer Application Note 2017
[13] Detection of three tumor biomarkers in human lung cancer serum using single particle inductively coupled plasma mass SPectrometry combined with magnetic immunoassay. Biyang Deng. State Key Laboratory for the Chemistry and Molecular Engineering of Medicinal Resources, School of Chemistry and Pharmaceutical Sciences, Guangxi Normal University, Guilin 541004, China. Spectrochimica Acta Part B 2020
[14] Monitoring the Uptake of Nanoparticles and Ionic/ Dissolved Gold by Fresh Water Algae using Single Cell ICP-MS. Ruth Merri ed1 Jamie Lead1 Chady Stephan2 1 Center for Environmental NanoScience and Risk (CENR), Arnold School of Public Health University of South Carolina, SC 2PerkinElmer Inc. Shelton, CT. PerkinElmer Application Note 2018
[15] Counting and recognizing single bacterial cells by a lanthanide encoding inductively coupled plasma mass SPectrometric approach. 王秋泉,廈門大學(xué) 化學(xué)系. Anal. Chem 2019
[16] A highly efficient introduction system for single cell- ICP-MS and its application to detection of copper in single human red blood cells. Biyang Deng,廣西師范大學(xué) 化學(xué)與藥物科學(xué)學(xué)院. Talanta 2019
[17] Single-Cell Quantification of a Highly Biocompatible Dinuclear Iridium(III)Complex for Photocatalytic Cancer Therapy.黃懷義,中山大學(xué)藥學(xué)院(深圳). Angewandte Chemie 2022
- 上下滑動(dòng),查看更多 -
相關(guān)閱讀
_
● 珀金埃爾默助力大規(guī)模儀器設(shè)備更新
?_
● 煥新升級(jí),科研賦能
?
?關(guān)注我們